Joint manipulations (adjustments) and mobilisations – spinal and extraspinal
The two main joint issues are joint pain and joint stiffness. Chiropractic manual adjustments – joint manipulation and mobilisation techniques focus on restoring the joints to full, pain free range motion.
Joint manipulations and mobilisations are commonly used in patients that experience back and neck pain, headaches, and pain in other areas of the body resulting from reduced range of motion in joints such as hips, knees, ankles, shoulders and wrists.
While there is a positive biomechanical effect to joint manipulations, there is also a positive neurological effect that influences how a person feels and functions (feel free to discuss this with your chiropractor).

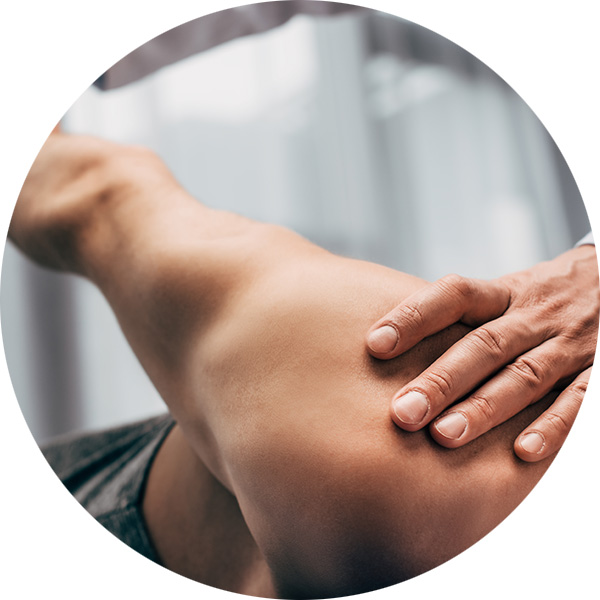
Soft Tissue Treatment – percussion therapy, massage techniques, myofascial release, cupping, stretching – MET and PNF, and IASTM techniques
Soft tissue treatment is an inclusive modality that covers several different treatment techniques. They aim to decrease muscle and fascial tension while increasing muscle elasticity and joint range of motion and to promote blood flow in the areas treated.
Soft tissue techniques are used in conditions of acute or chronic pain or injuries, trigger points, muscle spasms, and reduced joint range of motion. These techniques are also commonly used with headaches, back pain, joint pain, everyday aches and pains, and during prehabilitation and rehabilitation.
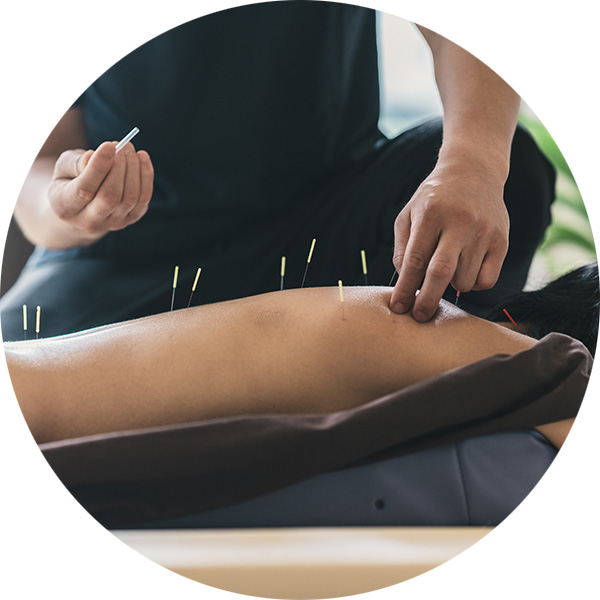
Dry Needling Therapy and Electrostimulation Dry Needling Therapy
The origins of dry needling stem from the ancient healing tradition of acupuncture. Dry needling is a procedure where a fine needle or acupuncture needle is inserted into the muscle. It is aimed at myofascial trigger points which are hyperirritable spots in skeletal muscle that can be associated with discomfort and or pain.
Electrostimulation Dry Needling is frequently use during dry needling treatment sessions. A stimulation machine is used to deliver a small amount of electrical current for electrical stimulation of the needles.
The benefits of dry needling and electrostimulation may include; pain relief, reduced muscle tension, improved joint range of motion, increased blood flow, faster wound healing and recovery time.
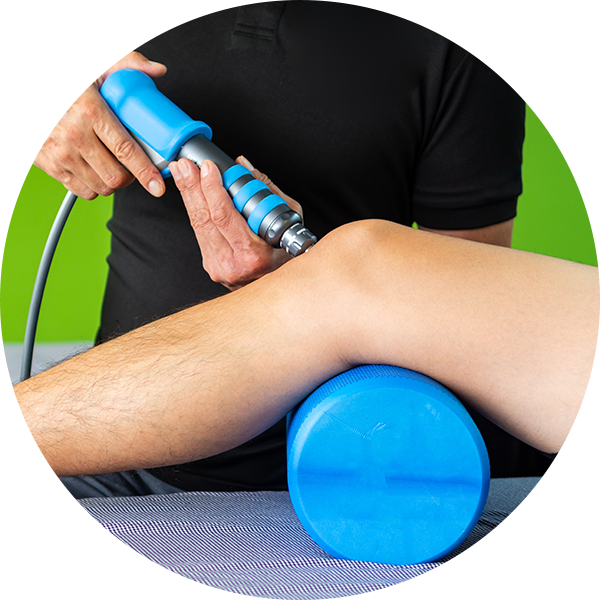
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy
(Shockwave Therapy)
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy, otherwise referred to as shockwave therapy is a specific, non-invasive treatment that involves delivery of high-energy sound and pressure waves into soft tissue to stimulate healing. This aims to reduce pain, increase blood flow, stimulate tendon, ligament and muscle repair and regeneration, and increase tissue healing at the cellular level.
Shockwave Therapy stimulates the body’s own immune system and is used in treating several musculoskeletal conditions including various types of fasciitis, tendinitis, bursitis, tendon, ligament and muscular injuries and bone disorders.
Some common conditions treated:
• Heel pain – plantar fasciitis
• Elbow pain – tennis elbow or golfer’s elbow
• Achilles tendonitis/tendinopathy
• Mechanical low back pain
• Knee pain – inflammation of the patellar tendon
• Shin pain / shin splints
• Shoulder pain – bursitis and calcification
• Muscular tension caused by painful muscle knots or trigger points
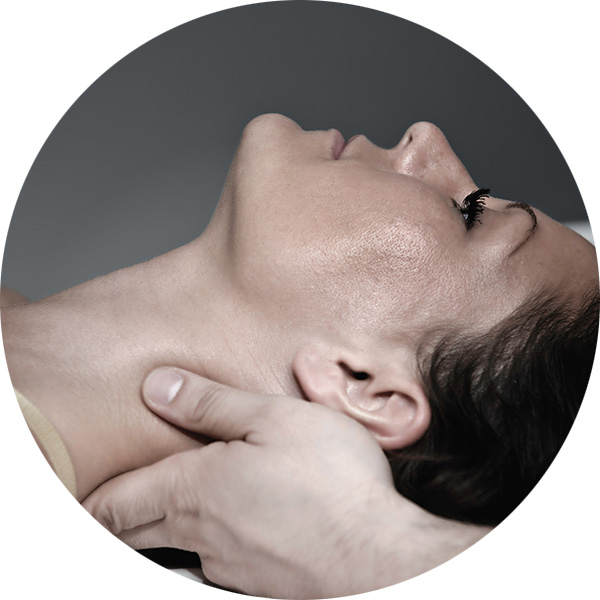
Low Force Techniques
Low force techniques utilise techniques from various treatment protocols such as – Sacro Occipital Technique (SOT), instrument assisted joint manipulations (Activator), Thompson drops, pelvic blocking, massage techniques and stretching.

Functional movement-based therapy: exercise – general, prehabilitation and rehabilitation
Passive treatments such as the above are good in and of themselves, however, for ongoing and lasting optimum health and function, good functional movement and exercise is a must!
Functional movement-based therapy is used to correct muscle, joint or postural imbalances that either cause or contribute to discomfort or pain, correct breathing patterns and provide people with the tools for proper bracing and movement strategies.
This is not limited to decreasing the current pain episodes but also at aimed at the prevention of further injury and reducing the risk of other injuries occurring in the future.
